Learnings from the Industry Targeted Cyber Attack Statistics of 2024
This article with historical data from the year 2024 helps in recognizing patterns in cyber attacks. Threat actors often reuse infrastructure, such as IP addresses and domains, across multiple campaigns. By analyzing past data, security teams can uncover these patterns and predict future attacks.
In 2024, cybersecurity has seen significant improvements, with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies enabling real-time threat identification and mitigation. This has improved efficiency in detecting anomalies and responding to cyber threats. Global collaboration has led to a decrease in large-scale cyberattacks such as ransomware. Public awareness and education about cybersecurity have increased in many countries, with more individuals and organizations adopting strong security practices like regular software updates, multi-factor authentication, and regular cybersecurity awareness trainings. New laws and regulations have been enacted to enhance cybersecurity standards and protect critical infrastructure. Quantum cryptography, a promising technology, is expected to revolutionize data security in the coming years.
Even though the technological advancements and collaboration are improving the cybersecurity of industries in many countries, it is also evident that the effective uses of AI technologies are being used by cybercriminals for more sophisticated cyberattacks. The SecureClaw Cyber Threat Advisory team studied more than 5000 international cyber attack news stories in various industries and created a most visible cyber threats trend considering sampling basis summary report, which will be discussed in this article. It is worth noting down that many organizations never report the cyber incident to media or government; hence, no one is able to identify exact statistics of the cyber attack trends. Few countries have strict enforcement of data privacy and other acts, where many organizations are forced to report cyber incidents to the government or even to the media. This article is an attempt to check the pulse of the cyber attack trends using whatever was evident via various sources of the cyber attack news.
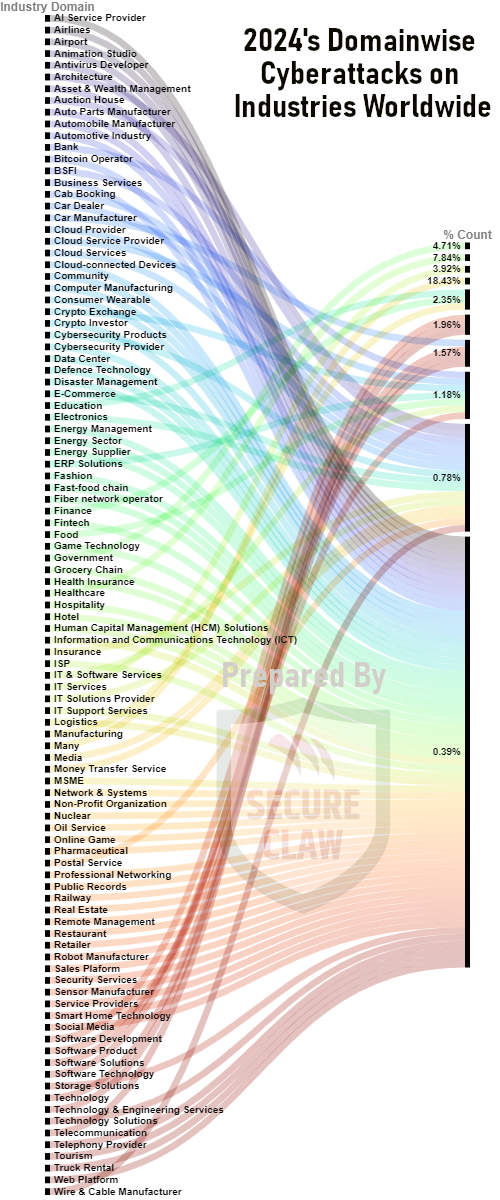
According to various cyberattack news sources worldwide, SecureClaw has observed that Healthcare, IT services, Manufacturing, and Software industries are among the maximum targets of cybercriminals. To summarize taking a snapshot of the count percentage of various industries as shown in Figure 1, here are a few statistics: Healthcare (7.84%), Government (4.71%), IT Services (3.92%), Education (2.35%), Finance (2.35%), Manufacturing (2.35%), Software Development (1.96%), Software Technology (1.96%), Telecommunication (1.96%), Car Manufacturer (1.57%), Software Solutions (1.57%), Technology (1.57%), Technology & Engineering Services (1.57%), Bank (1.18%), Cloud Service Provider (1.18%), Crypto Exchange (1.18%), ERP Solutions (1.18%), Food (1.18%), IT & Software Services (1.18%), and Software Product (1.18%).
This year, 2024, started with Mercedes-Benz Source Code and Subway's data leaked by hackers. While reaching the year-end, Japan Airlines experienced a cyberattack on December 26, 2024. The attack, which was a denial-of-service (DoS) attack, overwhelmed the airline's network with massive data transmissions, causing delays and system disruptions. At least 24 domestic flights were delayed by more than 30 minutes. Fortunately, the airline managed to restore its systems within a few hours, and flight operations returned to normal by December 27.
According to cyber news reached in the last three days of December 2024 in the USA, a ninth US telecommunications company, AT&T Inc. and Verizon Communications Inc., were targeted by the 'Salt Typhoon' campaign, a sophisticated cyberattack attributed to Chinese hackers. Also, the Volkswagen Data Breach caused 800,000 electric car owners' data to leak. On the last day of the year 2024, Thomas Cook (India) Ltd., a travel services provider, has reported a cyberattack on its IT infrastructure. Also almost at the same time Harley-Davidson, the iconic American motorcycle manufacturer, has reportedly fallen victim to a significant data breach orchestrated by a cybercriminal group known as "888." The group "888" is a relatively lesser-known entity in the cybercrime ecosystem. However, their recent activity has caught the attention of cyber threat intelligence analysts.
Figure 1: 2024's Domainwise Cyberattacks on Industries Worldwide by SecureClaw
Overview of World's Cyber Attack Trend of 2024:
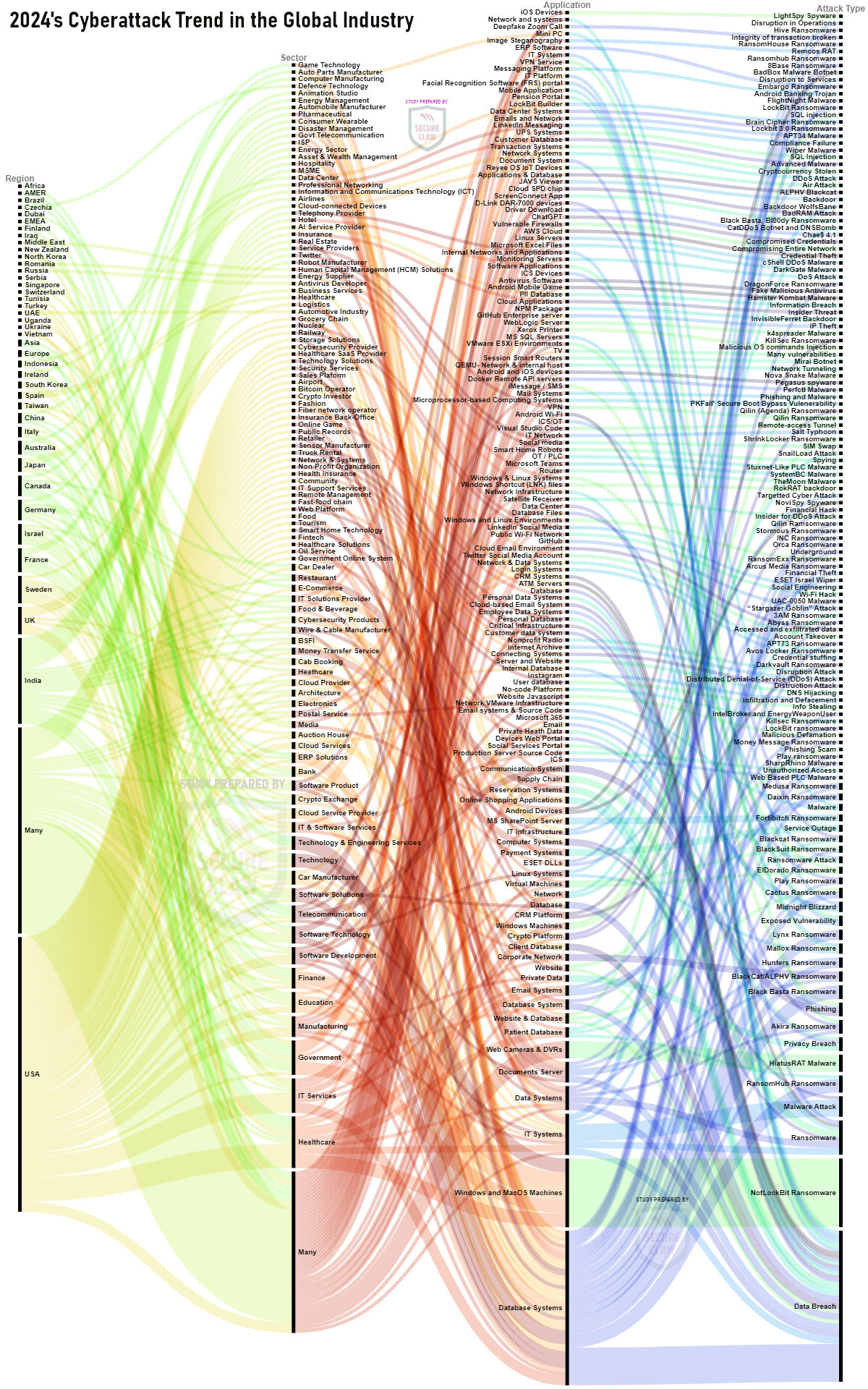
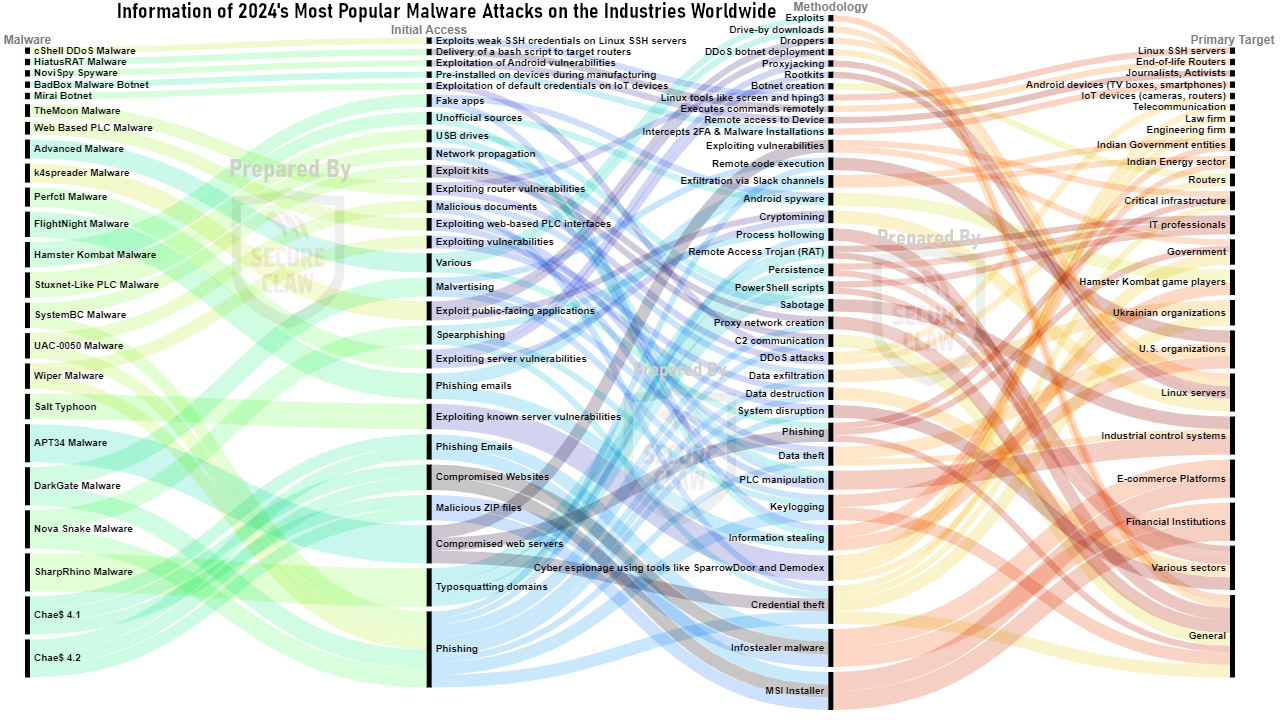
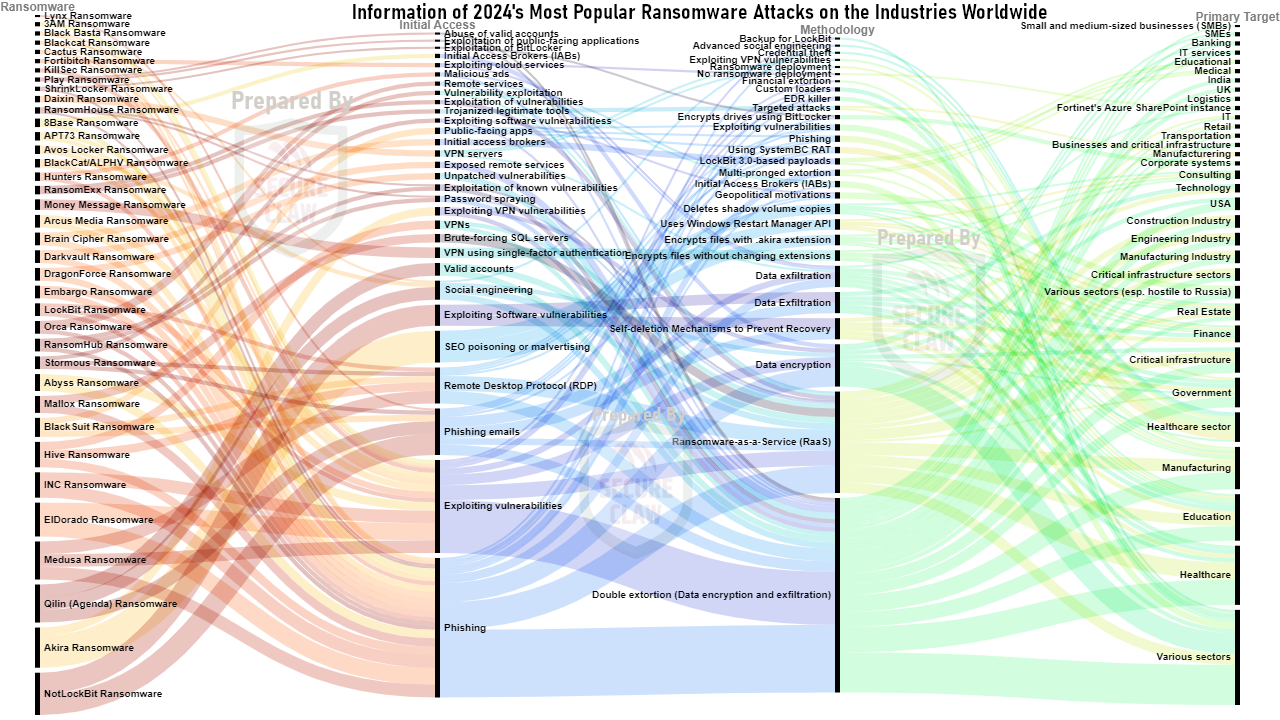
As shown in Figure 2, various variants of malware, ransomware, and many other cyber threats were observed in global cyber attack news in the year 2024.
Figure 2: World's Cyber Attack Trend of 2024
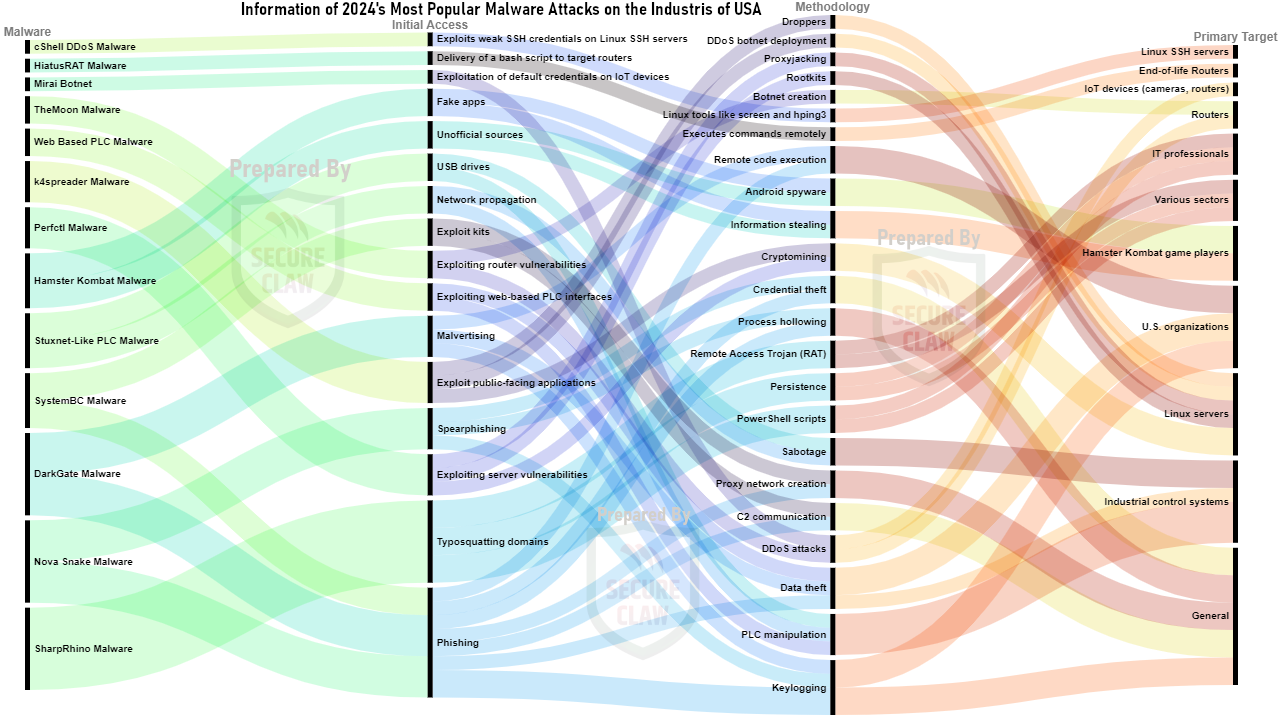
Overview of USA's Cyber Attack Trend of 2024:
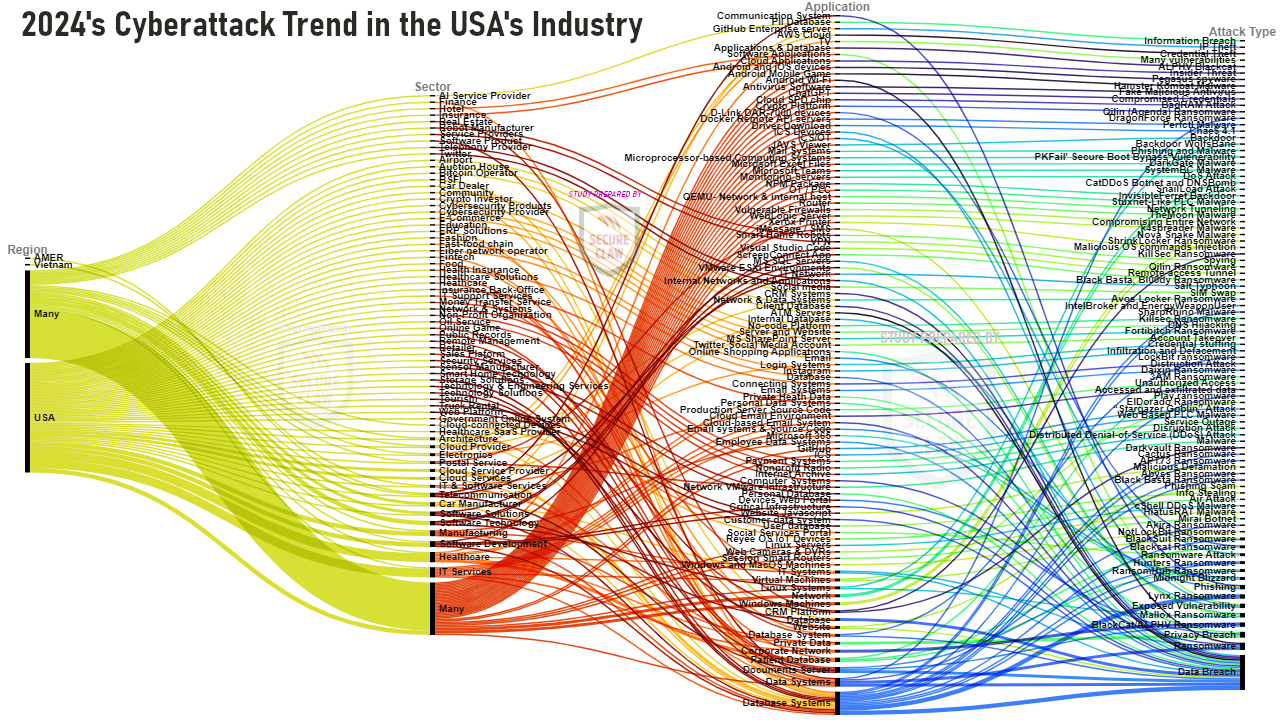
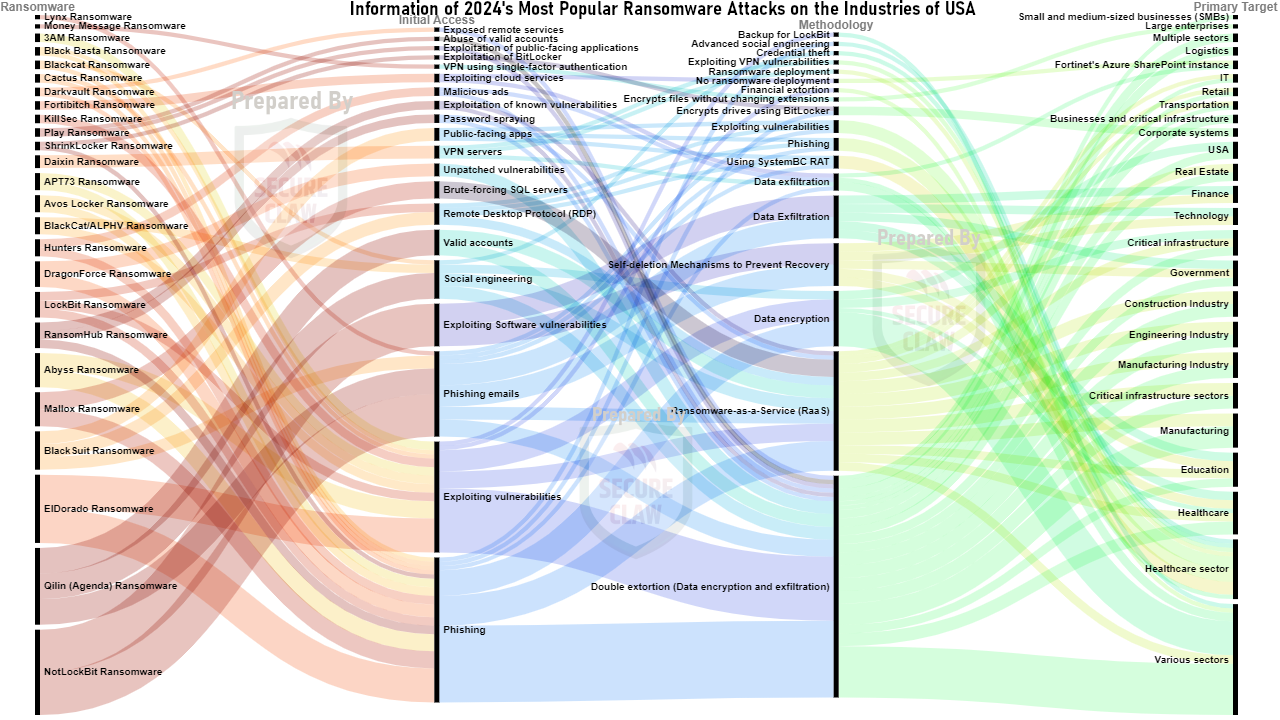
As shown in Figure 3, various variants of malware, ransomware, and many other cyber threats were observed in USA's cyber attack news in the year 2024.
Figure 3: USA's Cyber Attack Trend of 2024
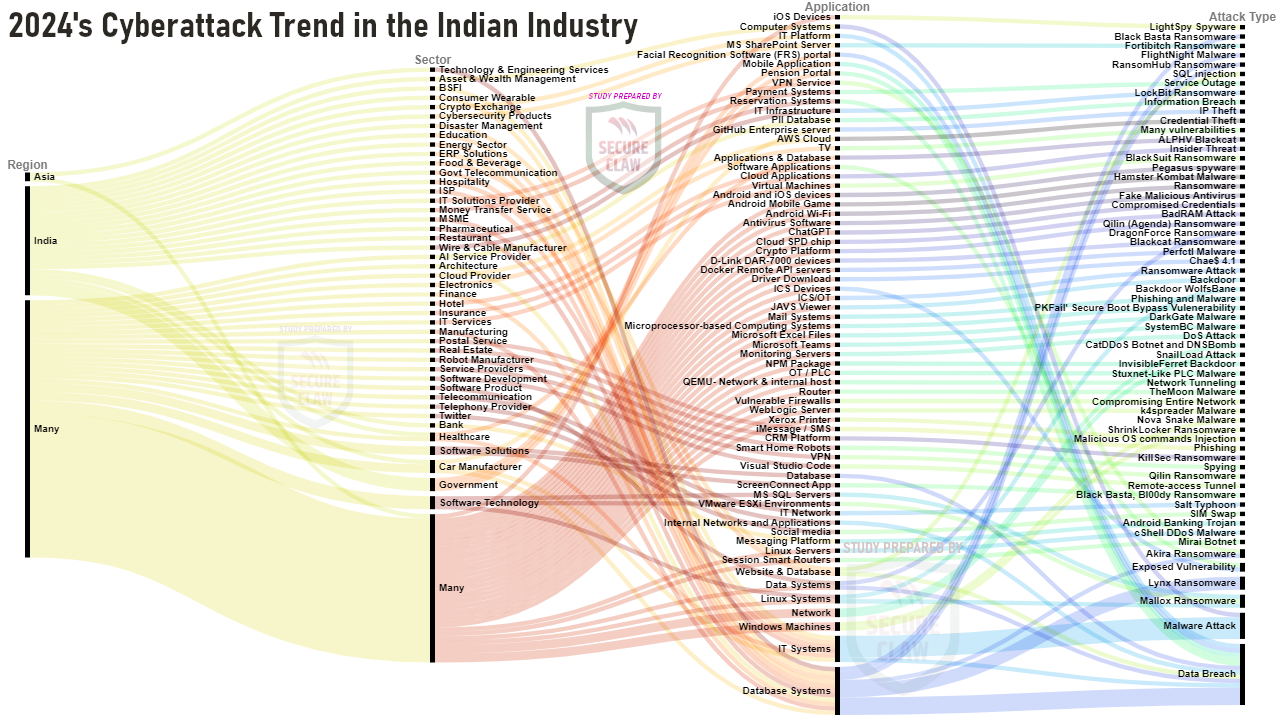
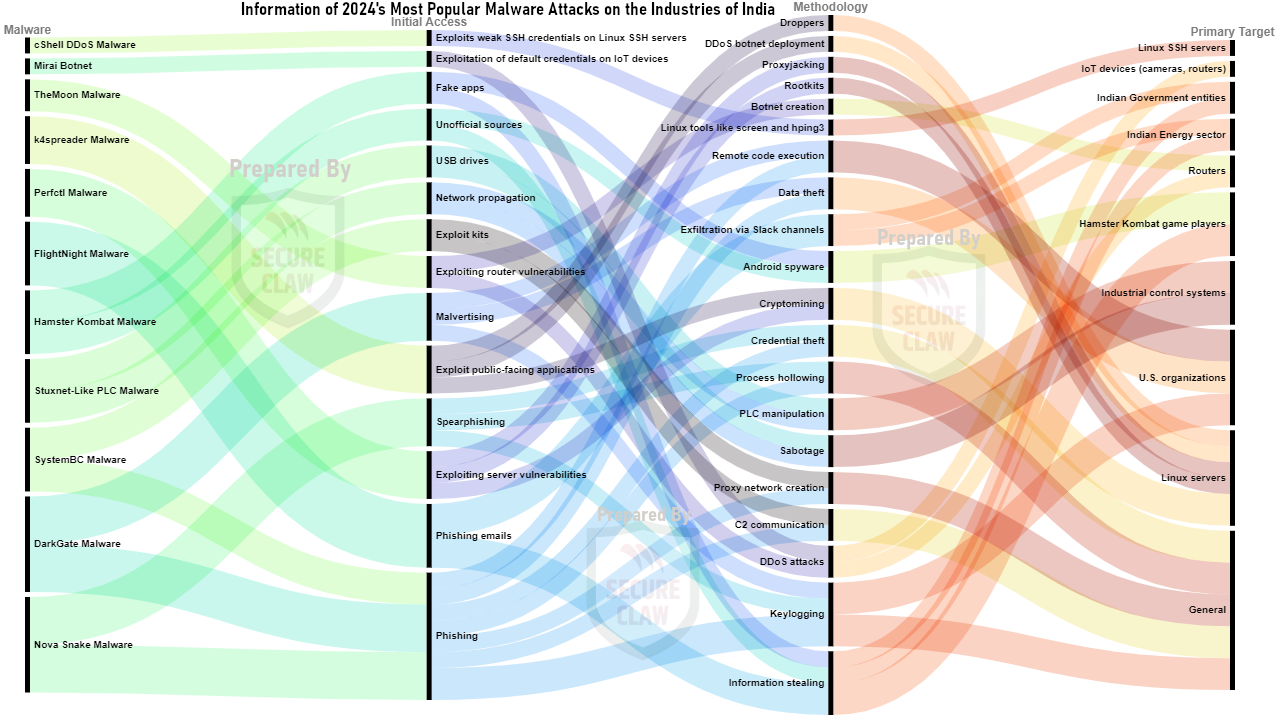
Overview of India's Cyber Attack Trend of 2024:
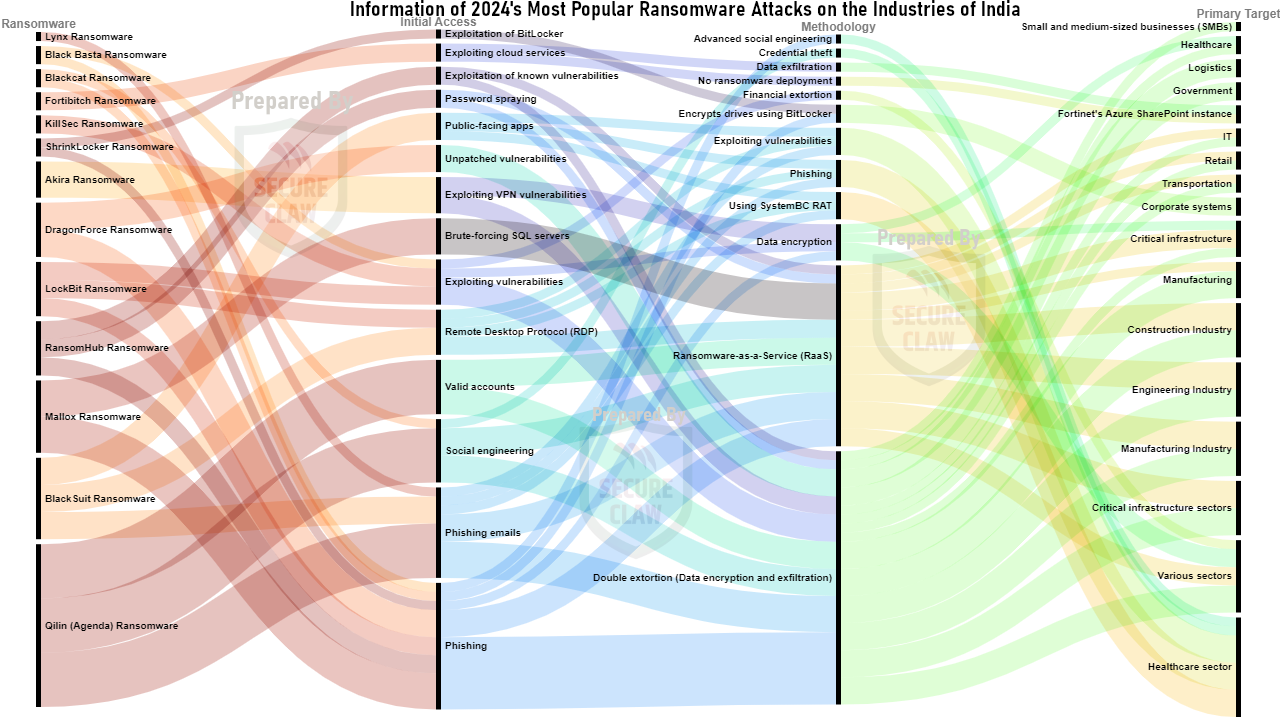
As shown in Figure 4, various variants of malware, ransomware, and many other cyber threats were observed in India's cyber attack news in the year 2024.
Figure 4: India's Cyber Attack Trend of 2024
Overview of Malware Attacks:
Malware means "malicious software" and refers to any software intentionally designed to cause harm to the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of any computer, server, client, OT, IoT, or network. Common types of malware include viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and rootkits. Malware can infiltrate systems through various methods such as phishing emails, infected files, malicious websites, or exploiting software vulnerabilities.
Once installed in a system, malware can steal, encrypt, or delete data. It can hijack core functions or even spy on user activity. It can even lock users out of their devices until a ransom is paid while working with a ransomware attack. Cybercriminals use malware for financial gain, data theft, espionage, or simply to cause disruption in the operations.
The cShell DDoS malware was recently discovered in December 2024. It targets poorly managed Linux SSH servers by exploiting weak SSH credentials and using Linux tools like screen and hping3 to execute sophisticated DDoS attacks. The error messages during the malware's installation process are written in German, suggesting a possible origin or operational clue.
The cShell DDoS malware was discovered in December 2024 by the AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC). It targets poorly managed Linux SSH servers by exploiting weak SSH credentials. Interestingly, error messages generated during the malware's installation process are written in German, which might hint at its origin or the background of its developers.
The Mirai botnet was first discovered in August 2016 by a white hat malware research group called MalwareMustDie. The botnet primarily targets Internet of Things (IoT) devices like routers, IP cameras, and home devices, turning them into remotely controlled bots for large-scale network attacks.
The BadBox malware botnet was first discovered in early 2023 on a T95 Android TV box available on Amazon. This malware is particularly insidious because it is often pre-installed on devices before they even reach consumers, making it difficult to detect and remove. The infection process is believed to occur either during the manufacturing stage or through a supply chain attack, where the malware is embedded in the device firmware.
The HiatusRAT malware has been in operation since July 2022. It is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that initially targeted outdated network edge devices but has since expanded to include various organizations in Taiwan and even reconnaissance against a U.S. government server. The malware has been actively scanning for vulnerabilities in web cameras and DVRs, particularly those of Chinese origin.
APT34 malware is said to have originated from Iran, and its first occurrence was observed in the year 2014. China-originated K4spreader malware's first occurrence was identified in the year 2024. FlightNight Malware and Hamster Kombat Malware are visible as new cyber threats in the year 2024. Since 2023, SharpRhino malware has been identified as active. While many malware's origin and first occurrence were not clearly known, DarkGate malware has existed since 2018, Nova Snake malware since 2020, Perfctl malware since 2021, SystemBC malware since 2019, and TheMoon malware since 2014. In 2024, few malware attacks were more visible in global cyber news; the diagram shows more analysis on how those work.
Apart from such malwares, there are few spywares active in cyberspace. Identified in 2024, NoviSpy is a sophisticated spyware targeting Android devices, primarily used for surveillance and data theft. It has been linked to the Serbian Security Intelligence Agency (BIA) and is known for its use against journalists and activists. It exploits vulnerabilities in Qualcomm products to gain unauthorized access to devices.
As shown in Figure 5, 6 and 7, few popular malwares of the year 2024 are displayed.
Figure 5: World's Popular Malware Attacks of 2024
Figure 6: USA's Popular Malware Attacks of 2024
Figure 7: India's Popular Malware Attacks of 2024
Overview of Ransomware Attacks:
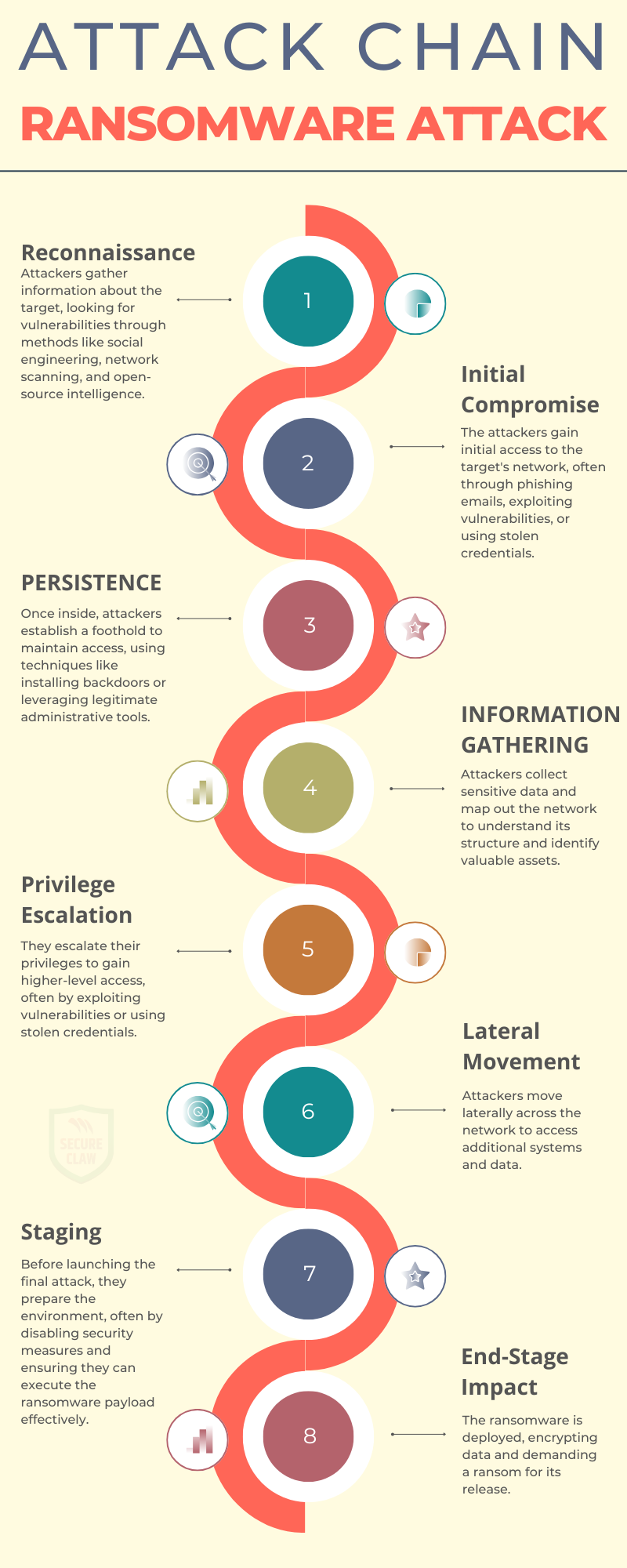
A ransomware attack is a type of cyberattack where malicious software, known as ransomware, encrypts or locks a victim's data or device. The attacker then demands a ransom payment to restore access. Ransomware attacks typically follow a series of eight stages, often referred to as the "attack chain."
It has been a very popular cyber attack for years. There are hundreds of such cybercriminal gangs active globally, and many of the ransomwares are named with the gang's name. While many ransomware gangs are underground and it is difficult to find their location or since how long they are active in the market, few reached in cyber-news, which can be assumed since then they are visible. APT73 Ransomware and Arcus Media Ransomware were visible in the year 2024. Since 2023, 3AM Ransomware, Abyss Ransomware, Akira Ransomware, BlackSuit Ransomware, and Cactus Ransomware were observed active globally. 8Base Ransomware, Black Basta Ransomware, Black Basta, Bl00dy Ransomware, Daixin Ransomware, Lockbit 3.0 Ransomware, Play Ransomware, RansomHouse Ransomware, and Stormous Ransomware were seen as first occurrences in the year 2022. Since 2021, Avos Locker Ransomware, BlackCat Ransomware, Hive Ransomware, Mallox Ransomware, and Medusa Ransomware were seen as new groups in global cyberattack news. RansomExx Ransomware has existed since 2020, and LockBit Ransomware has been active since 2019.
As shown in Figure 8, a ransomware attack gets performed in phases.
Figure 8: Ransomware Attacks Chain
Earlier ransomware attacks were only doing encryption of the victim systems or data, and they were demanding ransom for the decryption key. If the victim has a backup of the system or data, it was easily restorable back to normal. Then ransomware gangs improved their methodologies, starting double and triple extortion techniques. In double extortion, attackers not only encrypt data but also take a backup of it before encryption. Then they threaten to leak it online on the dark web or other platforms. Hence, only having a backup ready to restore doesn't help the victim. Further, in the case of triple extortion, attackers use stolen data to target the victim's customers or business partners by performing DDoS kinds of attacks. Ransomware attacks can be costly, with average costs reaching millions of dollars, excluding ransom payments. They are a significant threat due to their speed and the difficulty in tracing the attackers.
Many cybercriminal gangs are nation-state sponsored as well. Ransomware attacks are increasingly targeting critical infrastructure, including energy, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors. Conflicts between nations like Ukraine, Israel, and the South China Sea have fueled this trend. Factories and industrial facilities, relying on digital transformation, are prime targets. Traditional security methods are often insufficient. Ransomware attacks can disrupt economies, create political instability, and weaken adversaries' infrastructure. International initiatives and legal instruments are being developed to address this threat, improving cybersecurity standards and fostering international cooperation.
The Money Message ransomware first appeared in March 2023. This ransomware group quickly gained attention by demanding million-dollar ransoms from its victims. The ransomware targets both Windows and Linux systems, using sophisticated encryption techniques to lock files and demand payment for their release.
NotLockBit is a relatively new strain of ransomware that emerged in 2023. It is believed to be a variant of the LockBit ransomware family, which has been active since 2019. The LockBit group is known for its sophisticated ransomware attacks targeting various industries worldwide. NotLockBit, like its predecessor, encrypts victims' files and demands a ransom for their decryption.
In September 2024, cybercriminals invented a new ransomware methodology called "Fortibitch" to target Fortinet, a cybersecurity company. The breach resulted in unauthorized access and a leak of 440GB of customer data from Fortinet's Azure SharePoint repository. Fortinet confirmed that the breach did not involve ransomware deployment or access to their corporate network. The hacker, using the moniker "Fortibitch," leaked the data on the dark web after Fortinet refused to pay a ransom.
As shown in Figure 9, 10, and 11, few popular ransomware attacks of the year 2024 are displayed.
Figure 9: Popular Ransomware Attacks of 2024
Figure 10: USA's Popular Ransomware Attacks of 2024
Figure 11: India's Popular Ransomware Attacks of 2024
Actions Taken Against Cybercriminal Gangs:
In 2024, the FBI made significant strides in combating ransomware gangs. They conducted over 30 disruption operations targeting the infrastructure used by these groups. One notable operation, "Operation Cronos," involved international cooperation to disrupt the notorious LockBit ransomware gang.
One of the recent news December 2024, Raccoon Stealer malware operator gets 5 years in prison after guilty plea.
How can an organization be more cybersecure and cyber-resilient?:
Below are a few recommendations for the organizations to improve their cybersecurity posture.
-
Adopt a Defense-in-Depth Mechanism:
As more sophisticated cyber attacks have increased in many industry segments, just a couple of cybersecurity controls will not help. Organizations need to identify their mission-critical assets and need to adopt cybersecurity for various layers like data, application, host or endpoint, network, and physical perimeter, and then the overall governance cybersecurity layer.
There are many cybersecurity standards and frameworks available in the market helping in the structured implementation of the controls. American NIST and ISO 27001 (ISMS) are more popular in the world. Also, it is important to understand that 90% of the business population, which are small and medium businesses (SMBs), globally contribute to maximum employment and high value in GDP. In countries like India, SMBs are known as Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). In few countries these organizations also known as small and medium enterprises (SMEs). To reduce the cyberattack surface, these organizations can even adopt the Business Domain-Specific Least Cybersecurity Controls Implementation (BDSLCCI) framework, which is cost-effective, easy, and tailored to their business domain.
-
Cybersecurity Awareness Training for Employees:
Cyberattacks often stem from inadequate employee cybersecurity awareness. Effective training should cover phishing precautions, policies, and insider threats, with employee testing for effectiveness.
-
Beware of Supply Chain Attacks:
Third-party users, access to vendors and external applications should be monitored.
-
Monitor Your Network:
Regularly monitoring network logs and business transaction notifications is crucial for detecting malicious activities and taking necessary action to prevent them.
-
Regular Security Audits:
It is important to perform vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT) for the various IT assets of the organization, which should be part of the governance process, with processes enhanced as needed and compliance improved.
-
Incident Handing Process is Must:
Organizations need to be ready with a working plan for the unseen cyber incident. They need to track incidents as a report until permanent closure. Also, organizations need to prepare a business continuity plan (BCP) for any unseen circumstances, including natural disasters and cybercrimes.
-
Learn about Incident Reporting Process:
In the United States, under the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act (CIRCIA), covered entities must report cyber incidents to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) within 72 hours. Additionally, ransom payments must be reported within 24 hours.
For healthcare organizations in the USA, under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), healthcare entities must report breaches involving personal health information within 60 days. For the banking sector of the USA, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) requires banking organizations to report significant cyber incidents within 36 hours.
As per the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires organizations to report data breaches to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours.
In Australia, critical infrastructure entities must report cyber incidents within 72 hours under the Security of Critical Infrastructure (SOCI) Act.
The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), a part of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, has issued new guidelines under section 70B of the Information Technology Act, 2000, requiring all cybersecurity incidents to be reported within six hours of noticing or being informed about them. These guidelines are part of an effort to enhance the country's cybersecurity posture and ensure timely responses to potential threats.
Hence it is important to check where your organization is operating and the requirement of incident reporting according to the law of the land.
OVERVIEW of BDLSCCI Framework:
SecureClaw is a venture of Dr. Pawar, which is on the mission of cybersecuring small and medium companies worldwide, which are known as MSMEs, small and medium businesses (SMBs), or even small and medium enterprises (SMEs), depending on their size, revenue, and location. For this article, let us consider the word SMB, which represents any of these kinds of companies. With his decades of international experience and research studies during his doctorate from the Swiss School of Business and Management in Geneva, Switzerland, Dr. Pawar has invented a new cybersecurity framework popularly known as Business Domain Specific Least Cybersecurity Controls Implementation (BDSLCCI), which is more focused on these kinds of organizations. Apart from continuous research and enhancement in BDSLCCI to make it more beneficial to MSMEs, SecureClaw also provides various cybersecurity services, which include the Virtual Chief Information Security Officer (V-CISO), Source Code Security Review, which is popularly known as static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST), or vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT), as a few of its key offerings. These organizations have diverse experience in programming, telecom, and cybersecurity, which makes their expertise unique while designing solutions for their customers.
"Cybersecurity is right for every business, regardless of its size, location, or revenue! The BDSLCCI Cybersecurity Framework complies with the maximum cybersecurity controls's categories using a tailored list of controls, especially useful for micro, small, and medium enterprises known as SMEs, SMBs, MSMEs, or startup companies."
Dr. Shekhar A Pawar CEO, SecureClaw
Latest BDSLCCI Framework 3.0 has modified Defense in Depth (DiD) as well as Mission Critical Asset (MCA).
Visit www.BDSLCCI.com today to know more features and benefits!
During international research studies by Dr. Pawar, the top management of SMB companies from 19 different countries participated.
It was evident that there were three major problems faced by those companies.
- Small and medium-sized companies are not having enough funds or allocated budget for the implementation of hundreds of controls mandated by existing cybersecurity standards.
- These companies do not have skilled teammates or other resources to implement and maintain cybersecurity controls.
- Top management is not able to see the return on investment (RoI) for cybersecurity implementation, as the top priorities of such companies are not directly aligned with the recommended controls by existing cybersecurity standards or frameworks.
Dr. Pawar's research reveals that each SMB has a unique business domain and mission-critical asset (MCA) based on their sector. MCAs, such as data, information, or infrastructure, are crucial for a SMB's core business. For instance, healthcare MCAs might be Electronic Medical Record (EMR) software, while banking, financial services, and insurance (BSFI) MCAs might be financial records. MCAs can be information-related or even business function-related.
"Only antivirus or firewall kinds of cybersecurity controls are not enough to prevent cyber threats like ransomware. To protect an organization from sophisticated cyberattacks, it's important to implement defense in depth."
Dr. Shekhar A Pawar CEO, SecureClaw
As shown in Figure 12, BDSLCCI's defense-in-depth strategy helps in reducing the risk of ransomware attacks.
Figure 12: BDSLCCI Framework's Defense in Depth (DiD) helping to lower the risk of a Ransomware Attack
MCAs weigh confidentiality, integrity, and availability differently, and SMBs need cybersecurity controls. Defense in Depth (DiD) strategy addresses people, process, and technology. BDSLCCI framework provides recommendations for implementing DiD controls in parallel with MCA, designed by Dr. Pawar.
There are multiple ways to get BDSLCCI certification.
- SMB can self-assist by directly registering itself on the BDSLCCI web portal. The BDSLCCI web portal provides secured access to various data points and guidance provided by the logic of the BDSLCCI framework.
- SMB can identify a BDSLCCI member company, which is a certification body of BDSLCCI, authorized to provide BDSLCCI certificates as one of its services.
- SMB can even hire BDSLCCI-authorized freelancers who can assist them in their BDSLCCI certification journey, where the final audit will be done by SecureClaw and the BDSLCCI certification and transcript will be issued by SecureClaw.
The BDSLCCI offers certifications and assessments at three different levels. On the incremental order of control implementation, SMB can be more cybersecure while reaching BDSLCCI Level 3.
Any startup, even one employee company, or any medium-scale company with hundreds of employees can get a customized or tailored cybersecurity controls list using BDSLCCI. It offers an ascending order of controls, aiding top management in decision-making. In situations where organizations need to take the Data Privacy and Protection Acts of their nation seriously to avoid high penalties if a data breach happens, or even to avail of cyber insurance, or to simply have better confidence in their way of working and handling customers' critical assets, selecting SecureClaw's BDSLCCI will be a very good choice. SecureClaw has been deployed in many SMBs/ SMEs/ MSMEs and has received good market feedback.
Hope this article will help many organizations to understand the importance of cybersecurity controls implementation to protect their business, reputation, finance, and growth in the new year.

-helping-to-lower-the-risk-of-a-Ransomware-Attack.png)